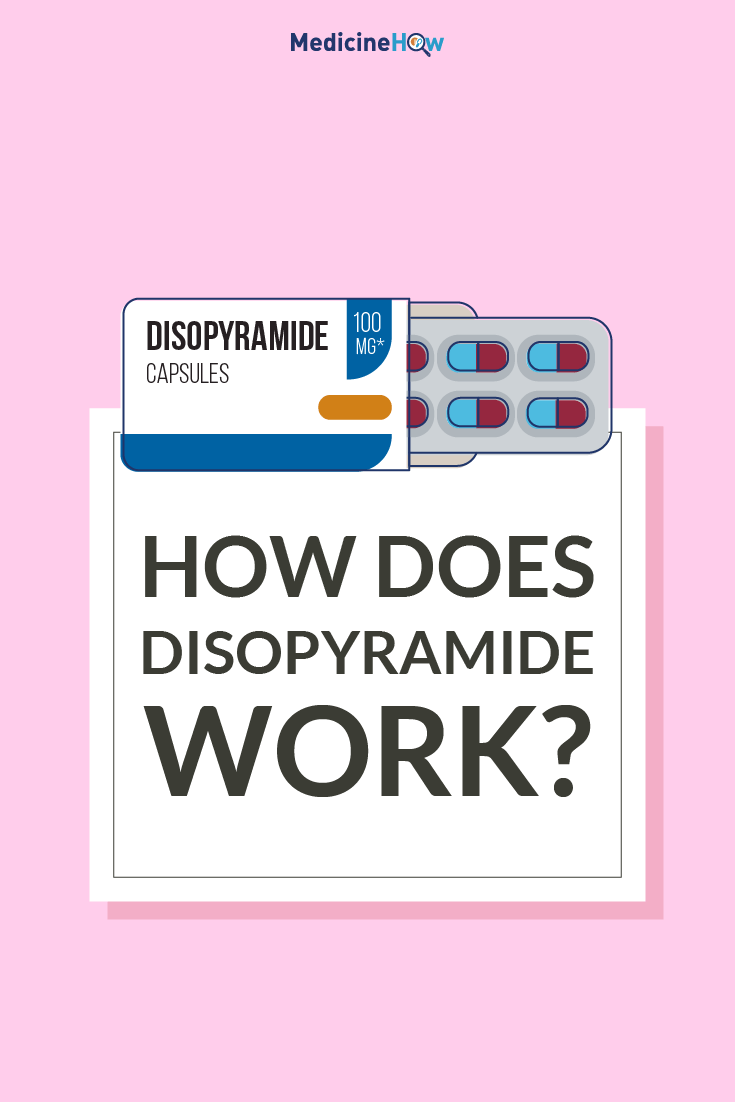
Disopyramide is a drug that works by affecting the conductivity of the heart muscle to control the rate and rhythm of the heart beating. It is usually used to treat ventricular tachyarrhythmias, particularly when other treatments haven’t been successful.
Brand Names and Doses
![]() Disopyramide is the generic name, the name of the active ingredient in the medication. You might also know it by the brand name, Rythmodan, which is the name given by the manufacturing company.
Disopyramide is the generic name, the name of the active ingredient in the medication. You might also know it by the brand name, Rythmodan, which is the name given by the manufacturing company.
It is available in two doses: 100 mg or 150 mg.
Most patients begin with a relatively high dose, such as 200 mg four times a day. As your body slowly builds up a supply of the drug, the dose can be reduced slightly (e.g. 100 mg four times a day).

What is it used for?
![]() Disopyramide is used to treat life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias. It is usually reserved for use after other medications have not had a sufficient effect.
Disopyramide is used to treat life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias. It is usually reserved for use after other medications have not had a sufficient effect.
It is less commonly used than other medications because it is not very convenient to take: you need to take a dose four times a day. For most people, it’s quite easy to forget a dose when you need to take it so often, which can disrupt the way the drug works.
How does disopyramide work?
![]() Disopyramide has several effects on the heart to control the rhythm of its beating.
Disopyramide has several effects on the heart to control the rhythm of its beating.
It prolongs the refractory period after the muscles have contracted so that it takes longer for the action potential to be reached again, slowing down the conduction of the heart.
It also increases the atrial ventricular node conductivity, as well as having a negative inotropic effect. Finally it can also decrease the automaticity in the Purkinje fibres.
Side Effects
![]() The more severe side effect of disopyramide is causing of worsening arrhythmias. It is important to monitor for adverse effect and abnormalities in the heart activity, as this required immediate medical attention.
The more severe side effect of disopyramide is causing of worsening arrhythmias. It is important to monitor for adverse effect and abnormalities in the heart activity, as this required immediate medical attention.
Other side effects may include:
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Urinary retention
- Shortness of breath
- Racing heart/palpitations
This is not a complete list of the side effects and you should see the medicine information leaflet for a complete list.
Precautions
![]() Some people should avoid taking disopyramide. For example, it’s best not to take it if you:
Some people should avoid taking disopyramide. For example, it’s best not to take it if you:
- Have previously experienced digoxin toxicity
- Are currently being treated with flecainide
- Have hypotension
- Have send of third-degree heart block, and you don’t have a pacemaker.
Additionally, there are some cases when it may still be the best option but you need to be more careful while taking it.
For example, it is more likely that disopyramide will have a negative effect on your heart and cause arrhythmias if you have an electrolyte imbalance in your blood (e.g. hypo- or hyperkalemia, hypomagnesia). It can also sometimes worsen glaucoma, cause urinary retention if you have prostatism and increase risk of hypoglycemia with diabetes treatment.
Finally, you may need to have a lower dose than usual if you have poor kidney or liver function, as your body is less effective at processing the drug and the concentration can build up more easily.
Drug Interactions
![]() Disopyramide can interact with some other drugs that you are taken and, depending on the situation, it may be best to avoid some combinations altogether.
Disopyramide can interact with some other drugs that you are taken and, depending on the situation, it may be best to avoid some combinations altogether.
Macrolides and increase the concentration of disopyramide in your body and increase the risk of side effects such as irregular heartbeat and hypoglycemia. For this reason, the combination should be avoided.
Phenytoin can decrease the concentration of disopyramide in your body so that it doesn’t work as well. Although, this can also increase the concentration of an active metabolite (the end product after your liver chemically “changes” the drug), which may lead to side effects. In this case, it’s best to watch the effect and increase or decrease the dose as needed.
Rifampicin and decrease the concentration and effect of disopyramide. If it is not have the desired effect, increasing the dose can help.

Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
![]() Disopyramide is probably safe to use in pregnancy and has been used by many pregnant women. However, it may have an oxytocic effect, which means it may stimulate contractions in the uterus and bring on or hasten childbirth.
Disopyramide is probably safe to use in pregnancy and has been used by many pregnant women. However, it may have an oxytocic effect, which means it may stimulate contractions in the uterus and bring on or hasten childbirth.
It is safe to be taken by pregnant women and is unlikely to have an adverse effect on the infant.
Pin it!