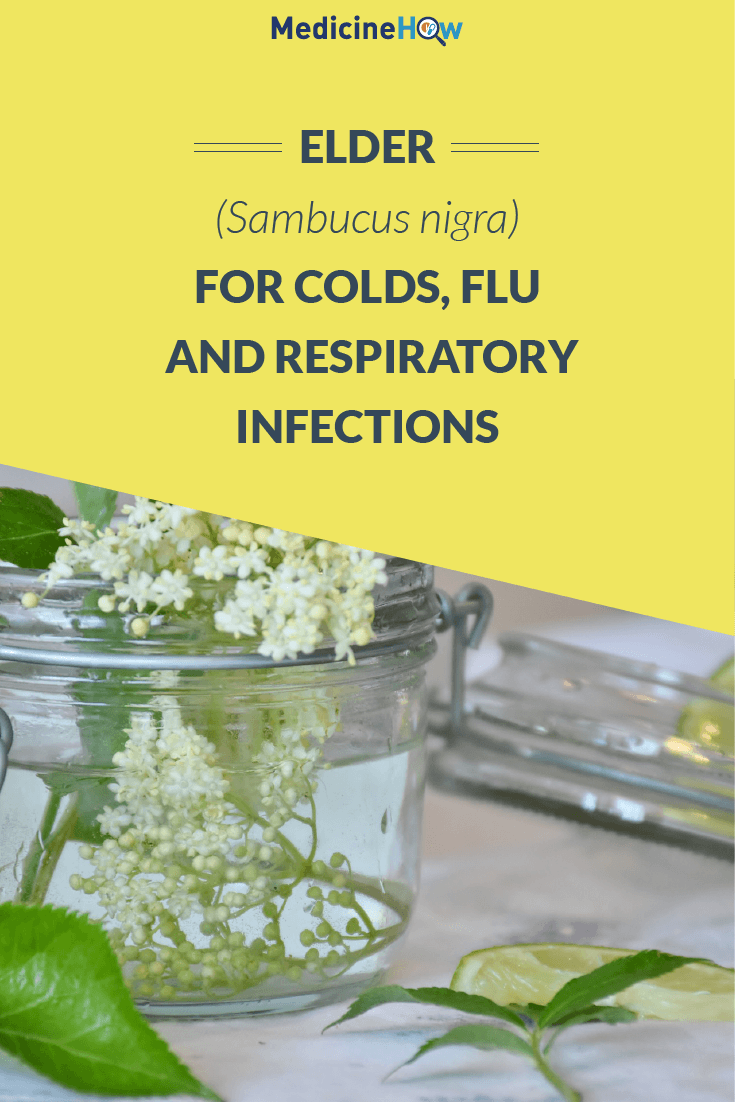
Elder (Sambucus nigra) has a wide range of medicinal effects that make it useful in the treatment of various health conditions.
Most notably, elderflower and elderberries are commonly used to help reduce the duration or severity of colds, flu and other respiratory infections, particularly when taken at the first sign of symptoms.
Elder can also be beneficial to reduce inflammation caused by arthritis or gout, as well as to improve circulation, support the nervous system and aid healing of physical wounds. To say it is a versatile herb would be an understatement!
Plant Names
The botanical name of elder is Sambucus nigra. This is the scientific name of the plant that is used all over the world, no matter what language that people speak. The name Sambucus originates from the sambuke, which is a Greek musical instrument made out elder wood.
Sambucus nigra refers to the type of elder plant with blackberries. There is another type called Sambucus racemosa, which has smaller red berried that are smaller and slightly toxic.
Elder is a member of the Adoxaceae or moschatel family of plants, alongside Adoxa and Viburnum. Previously, it was classified as part of the Caprifoliaceae or honeysuckle family.
It has many different common names, which are used to talk about the plant in everyday language. Some of the names that might be used to refer to elder include:
- Elder
- Black Elder
- Blue elderberry
- Bore Tree
- Bourtree
- Commom Elder
- Elderberry
- Elkhorn
- Sweet elder
Elder has also been used in traditional chinese medicine (TCM) where it is known as Jie gu mu.
Active Constituents

Elder is made up of many constituents that may impact the response that your body has to the herb. Additionally, different parts of the plant are made up of different things and, therefore, have distinct effects on the body.
The berries of the elder plant contain vitamin A, vitamin C, flavonoids, iron, anthocyanins, tannins and sambunigrine.
The flowers of the elder plant contain vitamin C, mucilage, flavonoids, volatile oils, quercetin, free fatty acids, triterpenes, phenolic acid, mineral sterols, sugars and tannins.
The leaves of the elder plant contain cyanogenic glycosides.
While the berries have some beneficial properties for the body, the flowers have wider use for medicinal purposes. In contrast, the leaves are not usually used internally because they can be toxic, although can be useful when applied topically to the skin of wounds or other injuries.
Taste and Energy

Elder is considered to have cool, pungent, slightly astringent and slightly sweet energies.
The taste of a plant can give some clues about the way that it will affect the body. Elder has a slightly sweet taste. This explains why it has a nourishing effect on the body and can be used to help soothe the nervous system.Medicinal Uses of Elder

Elder is sometimes known as the “medicine chest for country people” due to its vast range of medicinal effects and easy availability in nature. It has a long history of use, and was even recommended in the 4th century BC by Hippocrates.
Colds, Flu & Respiratory Infections
Both the flowers and the berries of the elder plant have diaphoretic and antiviral actions, which make them helpful in reducing colds, flu and respiratory infections.
Elder also has anti-inflammatory properties and can help to reduce congestion associated with sinus allergies and sinusitis as an anti-catarrhal and expectorant. It may help to reduce swelling of the mucus membranes, such as those in the respiratory tract to increase drainage and reduce nasal congestion.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Gout
Both elderflowers and elderberries contain anthocyanins that can help to reduce inflammation and the buildup of uric in the body and joints. For this reason, it can be helpful to relieve the symptoms of inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout.
It can also be used to reduce the inflammation linked to other health conditions, such as gingivitis, or inflammation of the gums.
Circulation
Elderflowers are thought to move energy and qi outward from the body, which can help to stimulate circulation and cause you to sweat more, which can be helpful to remove toxins and reduce fever.
Physical Injuries
The fresh leaves from the elder plant can be used externally to aid healing of physical injuries such as bruises, sprains and other wounds. This is because the leaves have vulnerary and astringent actions on the body, which encourages healing and toning in the area.
Stress and Anxiety
Elderflowers have relaxing nervine properties, which is useful to support the nervous system through stressful periods. It can help to soothe nerves and anxiety and may assist in reducing the symptoms of depression.
Harvest, Preparations and Dosages

When harvesting elderflower from the tree in early summer, you can remove the flowers in the cluster that they grow in by cutting them at the base of the stalk. It’s important to just remove the clusters that you need and not all of them, as the flowers will produce berries later on in the summer.
The berries ripen in late summer and should be fully ripe before harvesting because the green or unripe berries may contain mild toxins. As with the flowers, the entire cluster of berries can be cut from the tree and then the berries can be separated from the stems.
Once harvested, both elderflowers and elderberries can be dried or extracted in a tincture to be used when needed. A hot tea or tincture is the most common form of herbal elder to be taken for respiratory infections, such as a cold or flu.
Elderberries are commonly made into a tincture or syrup that is commonly taken at the first sign of a cold or flu to reduce the length and severity of the infection. This can interfere with the replication of the virus and strengthen the cell walls so that the virus cannot enter, so that you recover more quickly from the cold.
For external use, the leaves can be used mashed and used as a poultice for physical wounds or injuries. Alternatively, they can be made into an oil infusion and applied to the affected area.
Finally, the bark of the elder tree can be used as a purgative to induce a laxative effect, emetic to promote vomiting to expel toxins or diuretic to increase urine flow from the body. However, elder bark can be toxic if it is not properly prepared so it is essential for an experienced herbalist to be involved in using this.
Botanical Description, Environment and Sustainability

The elder tree can reach a height of up to ten meters (30 feet) and is native to Europe, North Africa and Western Asia, and currently also grows in North America. It prefers to grow in moist areas, such as in wetlands or with a river or creek nearby, although can also grow in forests, fields and the countryside. It grows readily in the wild and there are no known sustainability issues.
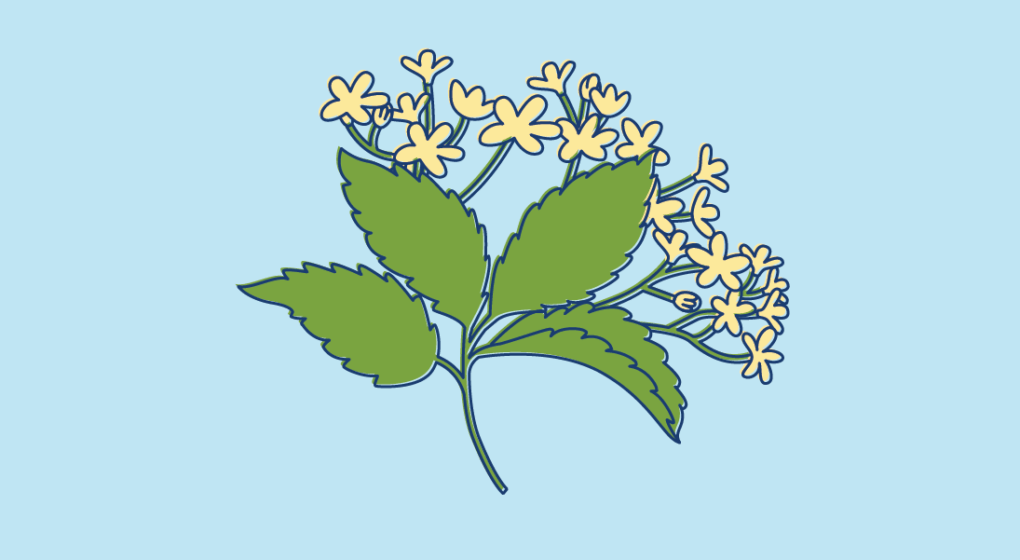
It has compound leaves, which are a group of leaves that grow from the same bud, growing opposite each other along the stem with one at leaf at the end. Each leaf has a serrated edge and an oblong shape. The stem of the plant is hollow with a pithy core.
Elderflowers have a creamy white color that grow in flat bunches that consist of hundreds of tiny flowers with five petals and strong fragrance. Each bunch may be up to 25 cm (10 inches) in diameter.
Elderberries are blue-black in color and grow in place of the flowers of the spring, so they appear in flat bunches with many berries on each one.
Pin it!